Choose your region, country/territory, and preferred language
How to use IDT's OligoAnalyzer™
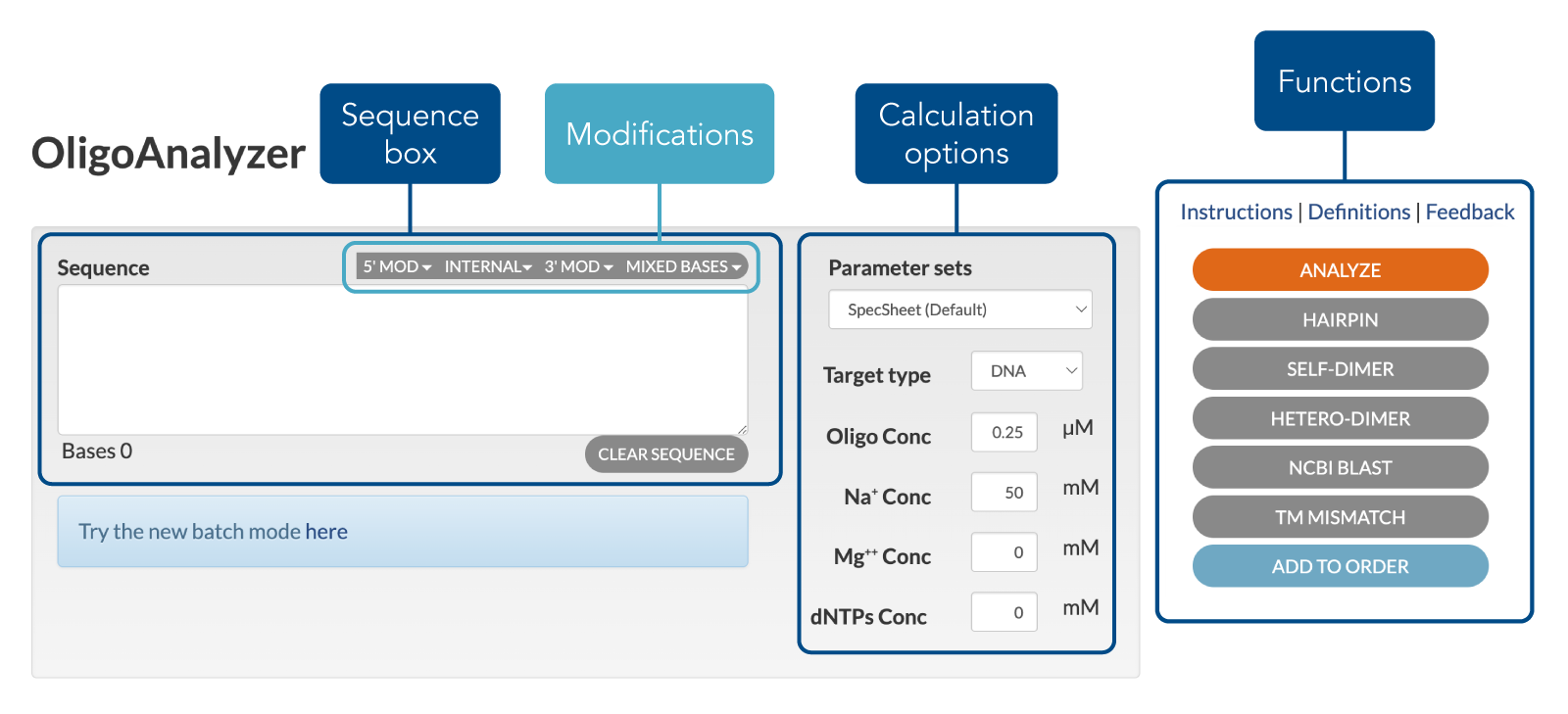
Step 1: Enter sequence to be analyzed in the sequence box
Enter a sequence into the sequence box at the top of the page. This version accepts the following base notations (Symbol '_' identifies base location):
- Standard Bases, (A, C, G, T, U, I) are not case sensitive.
- Mixed Bases, expressed in UPPERCASE.
- RNA, expressed as 'r_', for example rA, rU.
- 2' O-methyl RNA bases are entered as 'm_'.
- Locked nucleic acid bases (LNA) are entered as '+_'.
- Phosphorothioated DNA bases are entered as '_*'
- Phosphorothioated RNA bases are entered as 'r_*'.
- Phosphorothioated 2'-O-methyl RNA bases are entered as 'm_*'.
- Phosphorothioated LNA bases are entered as '+_*'.
Please note that rT and mT are not valid, and must be expressed as rU and mU instead.
How do I include standard mixed bases in my sequence?
To use a standard mixed base, type the letter of that mixed base into the sequence. The program will automatically recognize and include those base components in the calculations. Standard mixed base calculations are based on equimolar percentages. Click here, for IUB mixed base codes.
How do I include custom mixed bases in my sequence?
Custom mixed bases can be included in the sequence by typing the base percentages directly into the sequence box. Type, in parenthesis, a custom name followed by a colon and the base percentages, in ACGT order.
For example, (My base:10203040), will result in the following percentages: A=10, C=20, G=30, and T=40. It is also possible to type in only the percentages, without the custom name. (10203040) will have the same outcome as the previous example.
There can be more than one combination of percentages assigned to the same Mix Base.
How do I include standard chemical modifications in my sequence?
The modification tabs at the top righthand corner of the sequence box brings up a list of cataloged modifications— 5’, 3’, and internal modifications are available.
Click on the desired modification, and identify which modifications you want to be added.
You can use one of the two following methods:
- Click on the desired modification to be inserted. If the modification is at a 5’ or 3’ position then these modifications will automatically be added at 5' or 3' ends of the sequence, respectively. If you want to add internal modification, select the position within the sequence and then click the modification desired and it will automatically appear in the sequence box.
- Type the short sequence value name directly in the sequence box. Slashes must be included, for example "/3Bio/". It is also possible to copy and paste the sequence value from the list into the sequence box. You must include the slashes before and after the sequence value for the modification to be recognized by the calculator.
Please be aware that extinction coefficients for some modifications are unknown. Modifications are ignored when the complementary base is figured out and displayed in the results. However, for modifications that are base analogs, the complementary base is the native base. Complementary base to inosine is cytosine.
To quickly delete the contents of the sequence box, click the CLEAR SEQUENCE button.
Step 2: Modify calculation options
Select Target TypeSelect desired target type (DNA or RNA) that the oligo will be hybridizing to. The default target is DNA.
Enter oligo concentrationEnter oligo concentration in the box labeled Oligo Conc. The acceptable range of values is from 10-4 µM (100 pM) to 105 µM (100 mM). The default concentration is 0.25 µM. The TM model assumes that the oligo concentration is significantly larger (at least 6x) than the concentration of the complementary target, which is true in a majority of molecular biology experiments where the target concentration does not effect TM. See Definitions section for details.
Enter Na+ concentrationEnter monovalent (Na+) concentration in the box labeled Na+ Conc. Na+ concentration could be from 5–1500 mM (1.5 M). The default Na+ concentration is 50.0 mM.
Enter Mg++ concentrationEnter divalent (Mg++) concentration in the box labeled Mg++ Conc. Mg++ concentration could be from 0.01–600 mM; however the lower bound may not be lower than the oligo concentration multiplied by the oligo’s length. The default Mg++ concentration is 0.0 mM.
Enter dNTP concentrationEnter nucleotide triphosphate (dNTPs) concentration in the box labeled dNTPs Conc. dNTP concentration could be from 0.0–1000 mM (1.0 M); however the upper bound may not exceed 120% of the Mg++ concentration. The default dNTP concentration is 0.0 mM.
You must click any function button after these numbers have been altered in order for the changes to show in the results.
To easily return the above values to their default values, click the DEFAULT SETTINGS button.
Step 3: Select and click on a function button
After the above information has been entered, you may select and click any function button to initiate calculations.
- ANALYZE: Clicking on the ANALYZE button gives physical properties of the oligo sequence. The results will show a complementary sequence, oligo length, GC content, melting temperature, extinction coefficient, molecular weight, µg/OD, and nmol/OD.
- HAIRPIN: Clicking on the HAIRPIN button will bring the form that predicts oligo secondary structures using mFold algorithm (developed by Dr. Michael Zuker).
- SELF-DIMER: Clicking on the SELF-DIMER button will report possible duplexes and their stabilities when oligo hybridizes to itself.
- HETERO-DIMER: This function will examine possible duplexes when the oligo can anneal to any target sequence. Click on the HETERO-DIMER button and enter the target sequence.
- NCBI BLAST: Click on the NCBI Blast button to send your input sequence to NCBI 'search for short nearly exact matches' Blast page and initiate the search in the government database.
- TM MISMATCH: Click on the TM MISMATCH button, use the drop-down boxes to add 5' and 3' target bases flanking the duplex region. If a red target base is clicked, a dropdown box will appear and allow the user to select the desired mismatch. Only one mismatch can be introduced into the target sequence in this version. Specify hybridization temperature, which can be either exact complement Tm or other custom defined temperature. Enter the target concentration that can range from 0 µM (for unknown and very low concentration) to 105 µM (100 mM). Finally, hit CALCULATE button. Results will show melting temperatures, their difference, and percent of the exactly (perfectly) matched and mismatched strands bound to the target.
Have a question about terminology?
Click the Definitions link located above the sequence box to access information about IDT's Oligo Analyzer. All text subheadings on the calculator screen contain links to more information. A click on any link will take you to the part of the page that addresses the particular issue in question.
RUO23-2244_001